Start Over Again a Million Miles Away
JWST will orbit the sunday, a 1000000 miles away from Earth at the 2nd Lagrange point.
Webb Orbit
A Solar Orbit
The James Webb Infinite Telescope will not be in orbit around the Earth, like the Hubble Space Telescope is - information technology will actually orbit the Sunday, 1.5 million kilometers (1 million miles) away from the World at what is chosen the second Lagrange point or L2. What is special about this orbit is that it lets the telescope stay in line with the Earth as it moves effectually the Sunday. This allows the satellite's large sunshield to protect the telescope from the light and heat of the Sun and Earth (and Moon).

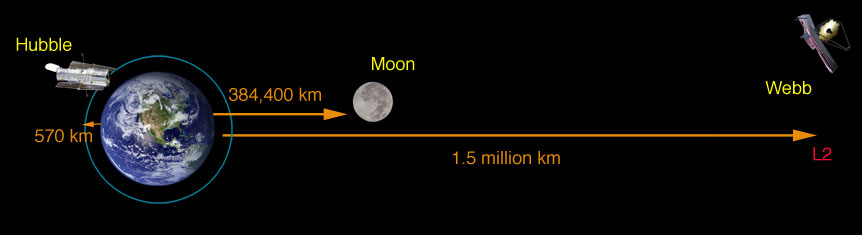
Animation of Webb'south Orbit
Why Does the Direction of the Earth and Sun Affair?
Webb primarily observes infrared light, which can sometimes be felt as heat. Because the telescope will be observing the very faint infrared signals of very distant objects, it needs to be shielded from any bright, hot sources. This likewise includes the satellite itself! The sunshield serves to split the sensitive mirrors and instruments from not just the Sun and Earth/Moon, but as well the spacecraft bus.
+
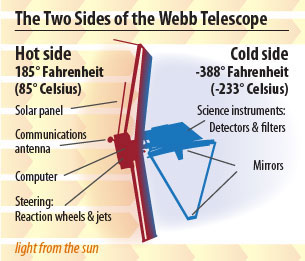
The telescope itself will be operating at nearly 225 degrees below zero Celsius (minus 370 Fahrenheit). The temperature departure between the hot and common cold sides of the telescope is huge - you could almost boil h2o on the hot side, and freeze nitrogen on the cold side!
To accept the sunshield exist effective protection (it gives the telescope the equivalent of SPF one million sunscreen) against the light and heat of the Sun/Earth/Moon, these bodies all have to be located in the same direction.
This is why the telescope will be out at the second Lagrange point.
What is L2?
Joseph-Louis Lagrange was an 18th century mathematician who found the solution to what is called the "iii-torso problem." That is, is in that location whatever stable configuration, in which three bodies could orbit each other, yet stay in the aforementioned position relative to each other? As information technology turns out, there are five solutions to this trouble - and they are called the five Lagrange points, afterwards their discoverer. At Lagrange points, the gravitational pull of two large masses precisely equals the centripetal strength required for a pocket-size object to movement with them. The L1, L2, and L3 points are all in line with each other - and L4 and L5 are at the points of equilateral triangles.
+
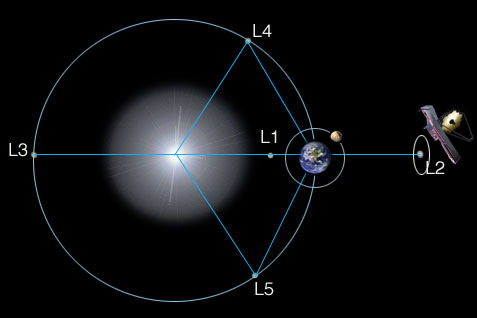
The first Sun-Earth Lagrange point, L1, is 1.v one thousand thousand km from the Earth towards the Sun, and there take been many solar observatories located here, including DSCOVR, Wind, SOHO, and ACE.
In that location have been other satellites out at Sunday-Globe L2, where Webb will be, including WMAP, Herschel, and Planck.
Some Technical Details: It is like shooting fish in a barrel for an object (like a spacecraft) at 1 of these five points to stay in place relative to the other two bodies (e.g., the Sunday and the Earth). In fact, L4 and L5 are stable in that objects there will orbit L4 and L5 with no assistance. Some small-scale asteroids are known to be orbiting the Sunday-Globe L4 and L5 points. However, L1, L2, and L3 are metastable then objects around these points slowly drift away into their own orbits effectually the Sun unless they maintain their positions, for case past using small-scale periodic rocket thrust. This is why L1, L2, and L3 don't "collect" objects similar L4 and L5 exercise.
Webb at L2
If Webb is orbiting the Sun further out than Earth, shouldn't information technology have more than than a twelvemonth to orbit the Sun? Commonly yes, but the remainder of the combined gravitational pull of the Sun and the World at the L2 point means that Webb will go on upward with the Globe equally information technology goes effectually the Sunday. The gravitational forces of the Lord's day and the Earth tin nigh hold a spacecraft at this point, so that it takes relatively fiddling rocket thrust to continue the spacecraft in orbit around L2.
And Webb will orbit around L2, not sit stationary precisely at L2. Webb's orbit is represented in this screenshot from our deployment video (below), roughly to calibration; it is really similar in size to the Moon'due south orbit around the Earth! This orbit (which takes Webb almost half-dozen months to complete once) keeps the telescope out of the shadows of both the Earth and Moon. Unlike Hubble, which goes in and out of Earth shadow every 90 minutes, Webb will accept an unimpeded view that will allow science operations 24/7.
Communicating with Webb
Webb's position out at L2 likewise makes it easy for the states to talk to information technology. Since it will always be at the same location relative to Earth-in the midnight sky about 1.five million km abroad - we can have continuous communications with it as the Earth rotates through the Deep Infinite Network (DSN), using 3 large antennas on the basis located in Australia, Spain and California. During routine operations, Webb will uplink command sequences and downlink data upwards to twice per mean solar day, through the DSN. The observatory can perform a sequence of commands (pointing and observations) autonomously. Typically, the Space Telescope Science Institute will upload a total week'southward worth of commands at a time, and make updates daily as needed.
How long will it take Webb to go to L2?
It volition accept roughly 30 days for Webb to attain the commencement of its orbit at L2, just it will have only 3 days to go every bit far away as the Moon's orbit, which is about a quarter of the manner there. Getting Webb to its orbit around L2 is like reaching the top of a hill by pedaling a bicycle vigorously only at the very start of the climb, generating enough free energy and speed to spend most of the manner benumbed up the colina so as to slow to a cease and barely make it at the height.
Timeline of Events After Launch:
+
- In the showtime hour: The ride to space, solar array deployment, and "gratis flying." The Ariane 5 launch vehicle will provide thrust for roughly 26 minutes subsequently a morning time liftoff from French Guiana. Moments later on second stage engine cut-off, Webb will dissever from the Ariane, which volition trigger the solar array to deploy within minutes so that Webb can start making electricity from sunshine and cease draining its battery. Webb volition rapidly establish its ability to orient itself and "wing" in space.
- In the first mean solar day: Mid-course correction to L2. Ariane will have sent Webb on a straight route to L2, without start orbiting Earth. During the first day, we volition execute the first and virtually of import trajectory correction maneuver using small rocket engines aboard Webb itself. Nosotros volition also release and deploy the high gain antenna to enable the highest bachelor rates of data communication as early as practical.
- In the first week: Sunshield deployment. Shortly after we execute a 2nd trajectory correction maneuver, we will offset the sequence of major deployments, beginning with the fore and aft sunshield pallets. The next step is separation of the spacecraft bus and telescope by extending the telescoping tower betwixt them. The tower will extend about 2 meters, and it is necessary at this signal in the sequence then that the rest of the sunshield deployment can proceed. Next, the sunshield membranes will be unpinned and the telescoping sunshield midbooms volition extend – commencement the port side and so the starboard side – pulling the membranes out with them. The last sunshield deployment step is tensioning of the membranes. In the meantime, other things similar radiators will be released and deployed.
- In the start calendar month:Telescope deployment, cooldown, instrument plow-on, and insertion into orbit around L2. During the second week subsequently launch we volition finish deploying the telescope structures past unfolding and latching the secondary mirror tripod and rotating and latching the two primary mirror wings. Note that the telescope and scientific instruments will commencement to cool chop-chop in the shade of the sunshield, just it will have several weeks for them to cool all the fashion down and reach stable temperatures. This cooldown volition be carefully controlled with strategically-placed electrical heater strips so that everything shrinks advisedly and then that water trapped inside parts of the observatory can escape every bit gas to the vacuum of space and non freeze as ice onto mirrors or detectors, which would degrade scientific performance. Nosotros will unlock all the primary mirror segments and the secondary mirror and verify that we can move them. Near the end of the first month, we will execute the last mid-course maneuver to insert into the optimum orbit around L2. During this time we will also ability-up the scientific musical instrument systems. The remaining five months of commissioning volition exist all about aligning the eyes and calibrating the scientific instruments.
- In the 2d, third and fourth months: Initial eyes checkouts, and telescope alignment. Using the Fine Guidance Sensor, we will point Webb at a single bright star and demonstrate that the observatory can acquire and lock onto targets, and we will accept data mainly with NIRCam. Merely because the primary mirror segments accept yet to be aligned to work as a single mirror, at that place will be up to 18 distorted images of the aforementioned unmarried target star. We will and then embark on the long process of aligning all the telescope optics, kickoff with identifying which primary mirror segment goes with which image by moving each segment i at a fourth dimension and catastrophe a few months later on with all the segments aligned as ane and the secondary mirror aligned optimally. Cooldown volition effectively end and the cryocooler will commencement running at its lowest temperature and MIRI tin can start taking good data likewise.
- In the fifth and sixth months: Calibration and completion of commissioning. We will meticulously calibrate all of the scientific instruments' many modes of operation while observing representative targets, and nosotros will demonstrate the ability to track "moving" targets, which are nearby objects like asteroids, comets, moons, and planets in our own solar arrangement. Nosotros will brand "Early Release Observations," to be revealed right after commissioning is over, that will showcase the capabilities of the observatory.
- After six months: "Science operations!" Webb will begin its scientific discipline mission and start to conduct routine science operations.
Source: https://jwst.nasa.gov/content/about/orbit.html

0 Response to "Start Over Again a Million Miles Away"
Post a Comment